An HCI researcher in love with Mixed Reality
2023

Exploring the Stability of Behavioral Biometrics in Virtual Reality in a Remote Field Study: Towards Implicit and Continuous User Identification through Body Movements
J.Liebers, C.Burschik, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM VRST '23, Christchurch, New Zealand
Behavioral biometrics has recently become a viable alternative method for user identification in Virtual Reality (VR). Its ability to identify users based solely on their implicit interaction allows for high usability and removes the burden commonly associated with security mechanisms. However, little is known about the temporal stability of behavior (i.e., how behavior changes over time),...
1st Joint Workshop on Cross Reality
H.Liang, H-C.Jetter, F.Maurer, U.Gruenefeld, M.Billinghurst, and C.AnthesPublished Workshop at IEEE ISMAR '23, Sydney, Australia
Cross Reality (CR) is an emerging technology that focuses on the concurrent usage of or the transition between multiple systems at different points on the reality-virtuality continuum (RVC), including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Virtuality (AV), and Augmented Reality (AR). CR has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential for revolutionizing various research and industry areas...
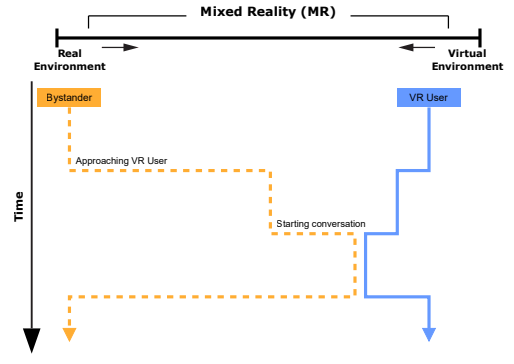
The Actuality-Time Continuum: Visualizing Interactions and Transitions Taking Place in Cross-Reality Systems
J.Auda, S.Faltaous, U.Gruenefeld, S.Mayer, and S.SchneegassPublished Workshop Paper at IEEE ISMAR '23, Sydney, Australia
In the last decade, researchers contributed an increasing number of cross-reality systems and their evaluations. Going beyond individual technologies such as Virtual or Augmented Reality, these systems introduce novel approaches that help to solve relevant problems such as the integration of bystanders or physical objects. However, cross-reality systems are complex by nature, and describing the interactions and transitions taking place is a challenging task...
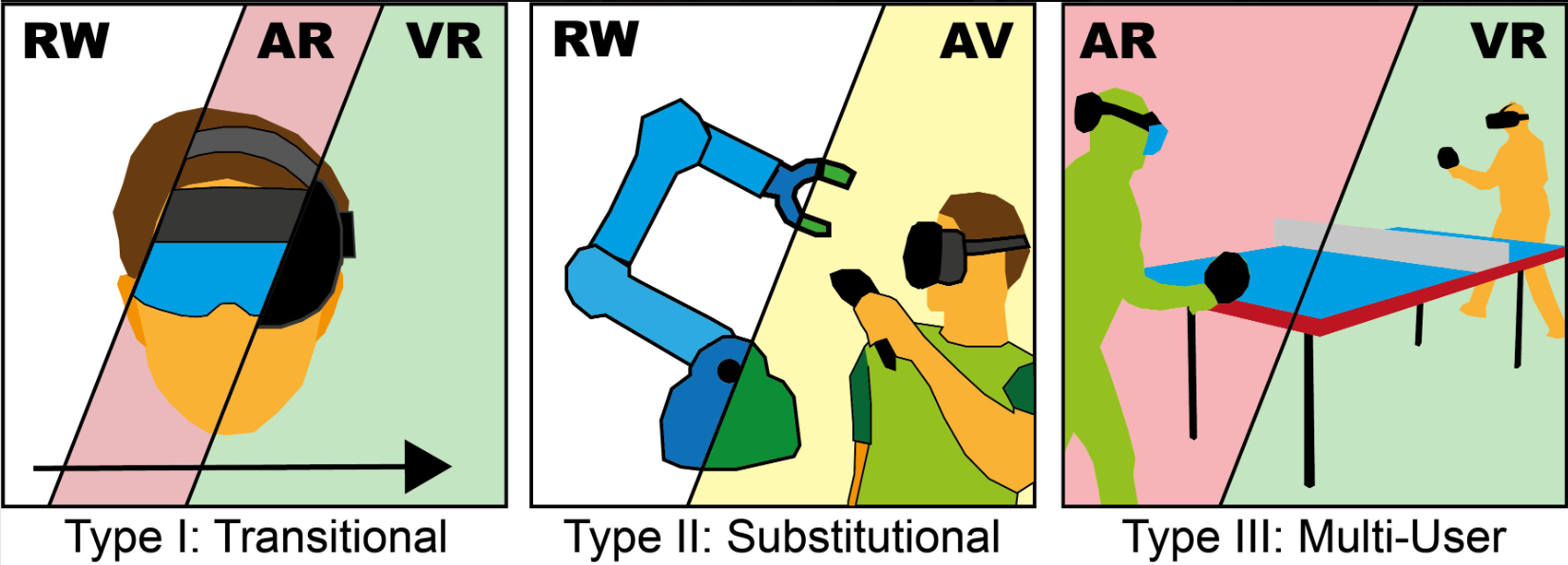
A Scoping Survey on Cross-Reality Systems
J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, S.Faltaous, S.Mayer, and S.SchneegassPublished Journal Article at ACM CSUR '23
Immersive technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) empower users to experience digital realities. Known as distinct technology classes, the lines between them are becoming increasingly blurry with recent technological advancements. New systems enable users to interact across technology classes or transition between them - referred to as cross-reality systems. Nevertheless, these systems are not well-understood. Hence, in this paper, we conducted a scoping literature review to classify and analyze cross-reality systems proposed in previous work...
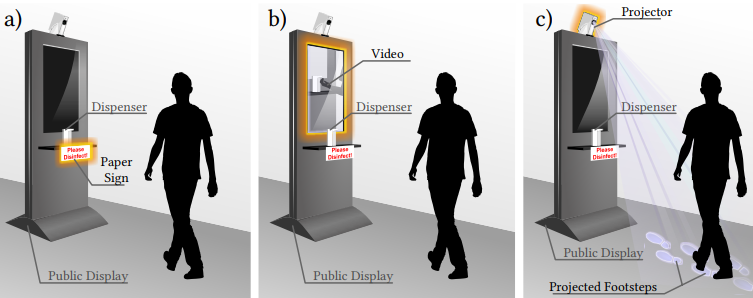
Don't Forget to Disinfect: Understanding Technology-Supported Hand Disinfection Stations
J.Keppel, M.Strauss, S.Faltaous, J.Liebers, R.Heger, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Journal Article at MobileHCI '23, Athens, Greece
The global COVID-19 pandemic created a constant need for hand disinfection. While it is still essential, disinfection use is declining with the decrease in perceived personal risk (e.g., as a result of vaccination). Thus this work explores using different visual cues to act as reminders for hand disinfection. We investigated different public display designs using (1) paper-based only, adding (2) screen-based, or (3) projection-based visual cues...
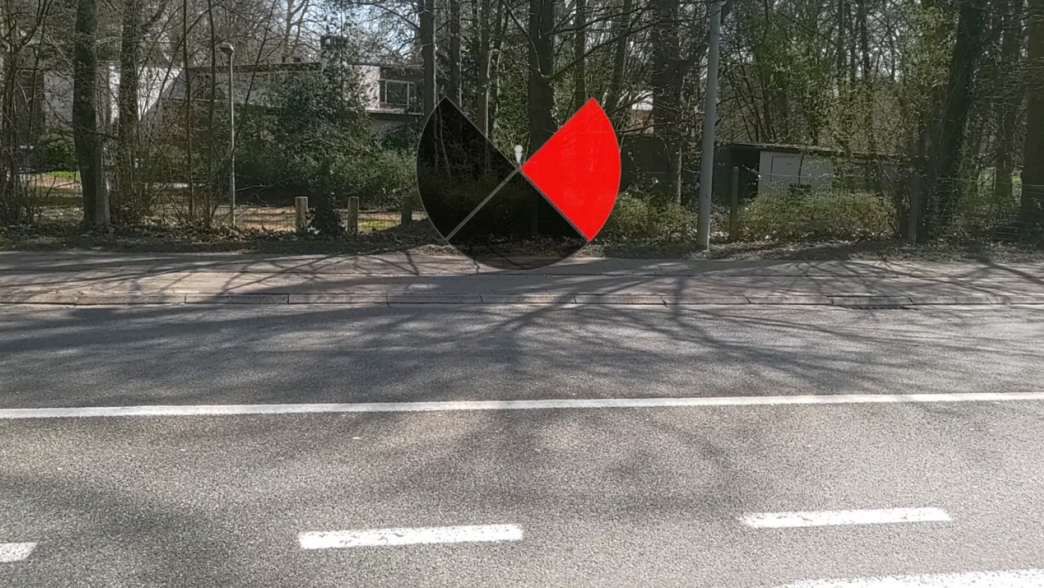

ARcoustic: A Mobile Augmented Reality System for Seeing Out-of-View Traffic
X.Zhang, X.Wu, R.Cools, A.L.Simeone, and U.GruenefeldPublished Conference Paper at AutoUI '23, Ingolstadt, Germany
Locating out-of-view vehicles can help pedestrians to avoid critical traffic encounters. Some previous approaches focused solely on visualising out-of-view objects, neglecting their localisation and limitations. Other methods rely on continuous camera-based localisation, raising privacy concerns. Hence, we propose the ARcoustic system, which utilises a microphone array for nearby moving vehicle localisation and visualises nearby out-of-view vehicles to support pedestrians...

“They see me scrollin”—Lessons Learned from Investigating Shoulder Surfing Behavior and Attack Mitigation Strategies
A.Saad, J.Liebers, S.Schneegass, and U.GruenefeldPublished Book Chapter at Springer Human Factors in Privacy Research
Mobile computing devices have become ubiquitous; however, they are prone to observation and reconstruction attacks. In particular, shoulder surfing, where an adversary observes another user's interaction without prior consent, remains a significant unresolved problem. In the past, researchers have primarily focused their research on making authentication more robust against shoulder surfing - with less emphasis on understanding the attacker or their behavior...

Pointing It out! Comparing Manual Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds between Desktop, Tablet, and Virtual Reality
C.Liebers, M.Prochazka, N.Pfützenreuter, J.Liebers, J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Journal Article at IJHCI '23
Scanning everyday objects with depth sensors is the state-of-the-art approach to generating point clouds for realistic 3D representations. However, the resulting point cloud data suffers from outliers and contains irrelevant data from neighboring objects. To obtain only the desired 3D representation, additional manual segmentation steps are required. In this paper, we compare three different technology classes as independent variables (desktop vs. tablet vs. virtual reality)...
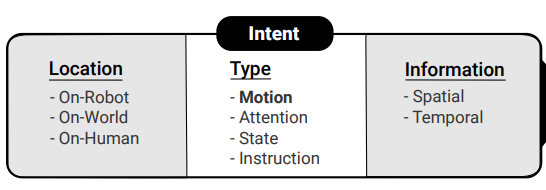
How to Communicate Robot Motion Intent: A Scoping Review
M.Pascher, U.Gruenefeld, S.Schneegass, and J.GerkenPublished Paper at ACM CHI '23, Hamburg, Germany
Robots are becoming increasingly omnipresent in our daily lives, supporting us and carrying out autonomous tasks. In Human-Robot Interaction, human actors benefit from understanding the robot’s motion intent to avoid task failures and foster collaboration. Finding effective ways to communicate this intent to users has recently received increased research interest. However, no common language has been established to systematize robot motion intent...

HaptiX: Vibrotactile Haptic Feedback for Communication of 3D Directional Cues
M.Pascher, T.Franzen, K.Kronhardt, U.Gruenefeld, S.Schneegass, and J.GerkenPublished Poster at ACM CHI '23, Hamburg, Germany
With non-Euclidean spaces, Virtual Reality (VR) experiences can more efficiently exploit the available physical space by using overlapping virtual rooms. However, the illusion created by these spaces can be discovered, if the overlap is too large. Thus, in this work, we investigate if users can be distracted from the overlap by showing a minimap that suggests that there is none...

Introduction to Authentication using Behavioral Biometrics
J.Liebers, U.Gruenefeld, D.Buschek, F.Alt, and S.SchneegassPublished Course at ACM CHI '23, Hamburg, Germany
The trend of ubiquitous computing goes in parallel with ubiquitous authentication, as users must confirm their identity several times a day on their devices. Passwords are increasingly superseded by biometrics for their inherent drawbacks, and Behavioral Biometrics are particularly promising for increased usability and user experience...
2022
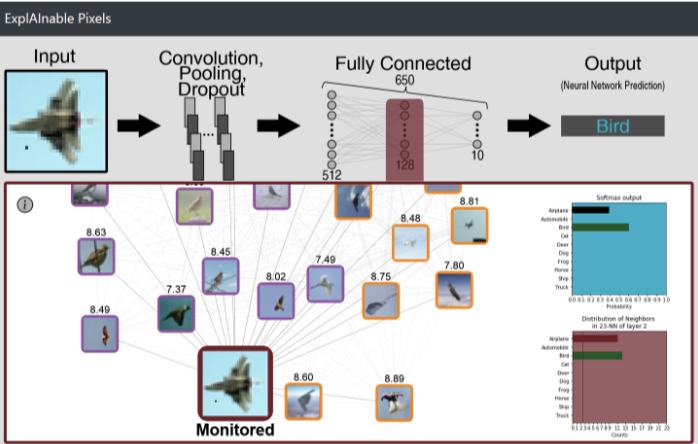
ExplAInable Pixels: Investigating One-Pixel Attacks on Deep Learning Models with Explainable Visualizations
J.Keppel, J.Liebers, J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM MUM '22, Lisbon, Portugal
🏆 Honorable Mention Award
Nowadays, deep learning models enable numerous safety-critical applications, such as biometric authentication, medical diagnosis support, and self-driving cars. However, previous studies have frequently demonstrated that these models are attackable through slight modifications of their inputs, so-called adversarial attacks...
Single-Sign-On in Smart Homes using Continuous Authentication
J.Liebers, N.Wittig, S.Janzon, P.Golkar, H.Moruf, W.Kontchipo, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Poster at ACM MUM '22, Lisbon, Portugal
Modern ubiquitous computing environments are increasingly populated with smart devices that need to know the identity of users interacting with them. At the same time, the number of authentications that a user needs to perform increases, as nowadays devices such as smart TVs require authentication which was not the case in earlier times...
Identifying Users by Their Hand Tracking Data in Augmented and Virtual Reality
J.Liebers, S.Brockel, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Journal Article at IJHCI '22
Nowadays, Augmented and Virtual Reality devices are widely available and are often shared among users due to their high cost. Thus, distinguishing users to offer personalized experiences is essential. However, currently used explicit user authentication (e.g., entering a password) is tedious and vulnerable to attack. Therefore, this work investigates the feasibility of implicitly identifying users by their hand tracking data...

A Systematic Analysis of External Factors Affecting Gait Identification
A.Saad, N.Wittig, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at IJBS '22, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Inertial sensors integrated into smartphones provide a unique opportunity for implicitly identifying users through their gait. However, researchers identified different external factors influencing the user's gait and consequently impact gait-based user identification algorithms. While these previous studies provide important insights, a holistic comparison of external factors influencing identification algorithms is still missing...
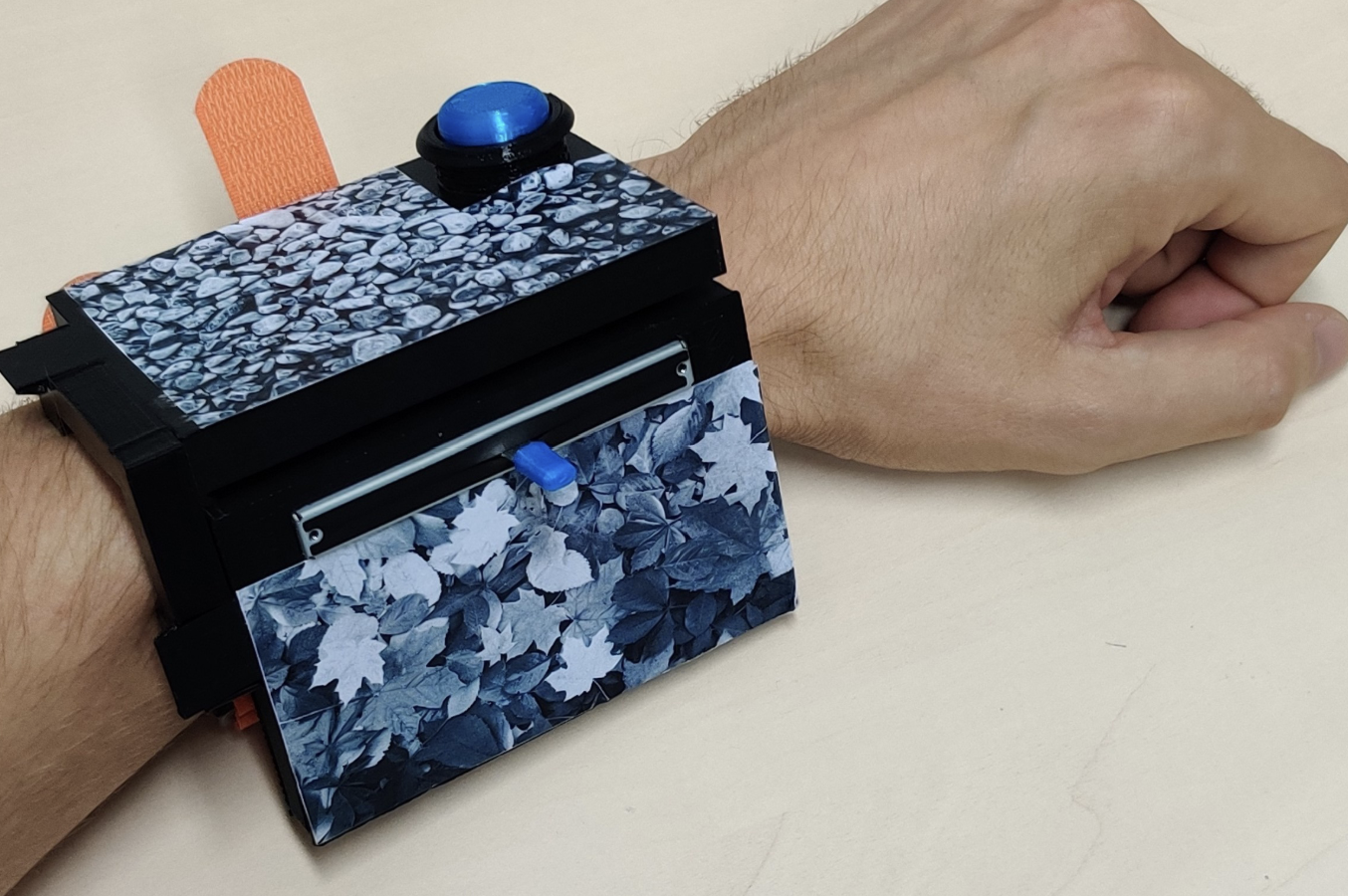

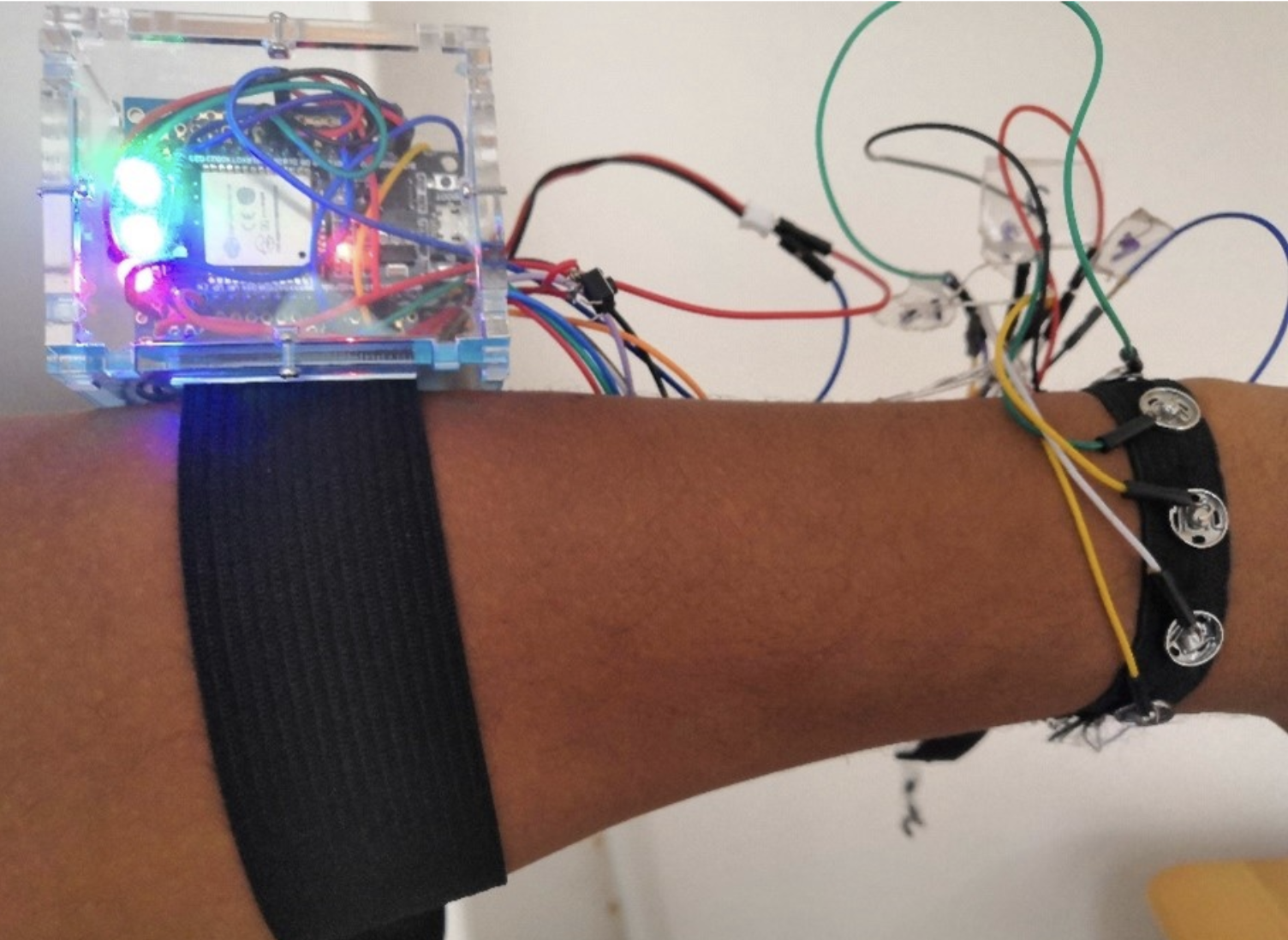
ARm Haptics: 3D-Printed Wearable Haptics for Mobile Augmented Reality
U.Gruenefeld, A.Geilen, J.Liebers, N.Wittig, M.Koelle, and S.SchneegassPublished Journal Article at MobileHCI '22, Vancouver, Canada
Augmented Reality (AR) technology enables users to superpose virtual content onto their environments. However, interacting with virtual content while mobile often requires users to perform interactions in mid-air, resulting in a lack of haptic feedback. Hence, in this work, we present the ARm Haptics system, which is worn on the user's forearm...
Reflecting on Approaches to Monitor User’s Dietary Intake
J.Keppel, U.Gruenefeld, M.Strauss, L.Gonzalez, O.Amft, and S.SchneegassPublished Workshop Paper at MobileHCI '22, Vancouver, Canada
Monitoring dietary intake is essential to providing user feedback and achieving a healthier lifestyle. In the past, different approaches for monitoring dietary behavior have been proposed. In this position paper, we first present an overview of the state-of-the-art techniques grouped by image-and sensor-based approaches....

Investigating the Influence of Gaze-and Context-Adaptive Head-up Displays on Take-Over Requests
H.Detjen, S.Faltaous, J.Keppel, M.Prochazka, U.Gruenefeld, S.Sadeghian, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at AutoUI '22, Seoul, South Korea
In Level 3 automated vehicles, preparing drivers for take-over requests (TORs) on the head-up display (HUD) requires their repeated attention. Visually salient HUD elements can distract attention from potentially critical parts in a driving scene during a TOR. Further, attention is (a) meanwhile needed for non-driving-related activities and can (b) be over-requested...
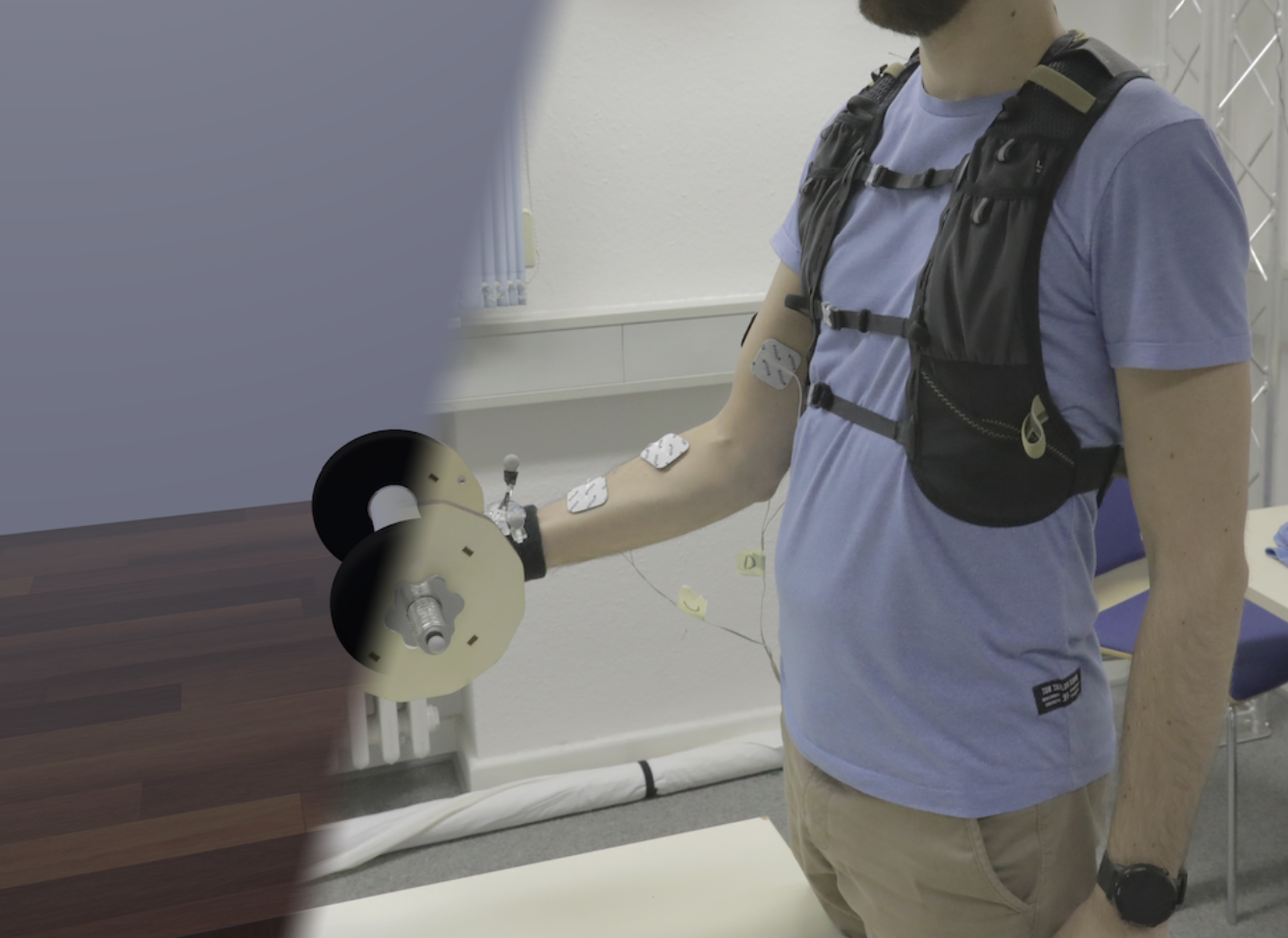
Give Weight to VR: Manipulating Users’ Perception of Weight in Virtual Reality with Electric Muscle Stimulation
S.Faltaous, M.Prochazka, J.Auda, J.Keppel, N.Wittig, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at Mensch und Computer '22, Darmstadt, Germany
Virtual Reality (VR) devices empower users to experience virtual worlds through rich visual and auditory sensations. However, believable haptic feedback that communicates the physical properties of virtual objects, such as their weight, is still unsolved in VR. The current trend towards hand tracking-based interactions, neglecting the typical controllers, further amplifies this problem...

Investigating the Challenges Facing Behavioral Biometrics in Everyday Life
A.Saad, and U.GruenefeldPublished Workshop Paper at Mensch und Computer '22, Darmstadt, Germany
The rapid progress of ubiquitous devices’ usage is faced with equally rapid progress of user-centered attacks. Researchers considered adopting different user identification methods, with more attention towards the implicit and continuous ones, to maintain the balance between usability and privacy...

Understanding Shoulder Surfer Behavior and Attack Patterns Using Virtual Reality
Y.Abdrabou, R.Rivu, T.Ammar, J.Liebers, A.Saad, C.Liebers, U.Gruenefeld, P.Knierim, M.Khamis, V.Mäkelä, S.Schneegass, and F.AltAccepted Paper at ACM In-Cooperation AVI '22, Rome, Italy
In this work, we explore attacker behavior during shoulder surfing. As such behavior is often opportunistic and difficult to observe in real world settings, we leverage the capabilities of virtual reality (VR). We recruited 24 participants and observed their behavior in two virtual waiting scenarios: at a bus stop and in an open office space...
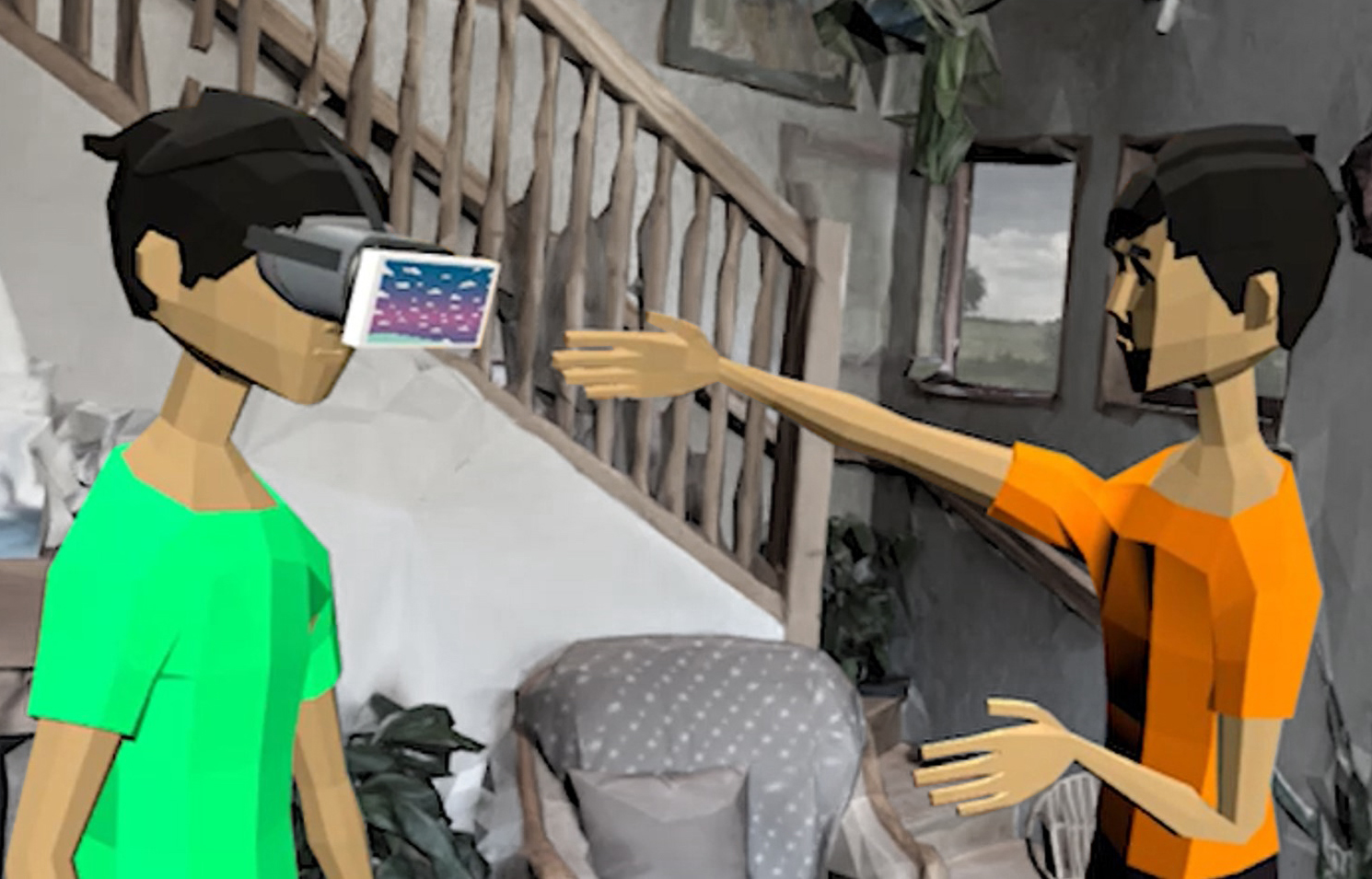

VRception: Rapid Prototyping of Cross-Reality Systems in Virtual Reality
U.Gruenefeld, J.Auda, F.Mathis, S.Schneegass, M.Khamis, J.Gugenheimer, and S.MayerPublished Paper at ACM CHI '22, New Orleans, USA
🏆 Honorable Mention Award
Cross-reality systems empower users to transition along the reality-virtuality continuum or collaborate with others experiencing different manifestations of it. However, prototyping these systems is challenging, as it requires sophisticated technical skills, time, and often expensive hardware. We present VRception, a concept and toolkit for quick and easy prototyping of cross-reality systems...

If The Map Fits! Exploring Minimaps as Distractors from Non-Euclidean Spaces in Virtual Reality
J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Poster at ACM CHI '22, New Orleans, USA
With non-Euclidean spaces, Virtual Reality (VR) experiences can more efficiently exploit the available physical space by using overlapping virtual rooms. However, the illusion created by these spaces can be discovered, if the overlap is too large. Thus, in this work, we investigate if users can be distracted from the overlap by showing a minimap that suggests that there is none...
Mask removal isn’t always convenient in public! -- The Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Device Usage and User Authentication
A.Saad, U.Gruenefeld, L.Mecke, M.Koelle, F.Alt, and S.SchneegassPublished Poster at ACM CHI '22, New Orleans, USA
The ongoing Covid-19 pandemic has impacted our everyday lives and demands everyone to take countermeasures such as wearing masks or disinfecting their hands. However, while previous work suggests that these countermeasures may profoundly impact biometric authentication, an investigation of the actual impact is still missing. Hence, in this work, we present our findings from an online survey (n=334)...

Understanding Challenges and Opportunities of Technology-Supported Sign Language Learning
S.Faltaous, T.Winkler, C.Schneegass, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM In-Cooperation AHs '22, Munich, Germany
Around 466 million people in the world live with hearing loss, with many benefiting from sign language as a mean of communication. Through advancements in technology-supported learning, autodidactic acquisition of sign languages, e.g., American Sign Language (ASL), has become possible. However, little is known about the best practices for teaching signs using technology...

The Butterfly Effect: Novel Opportunities for Steady-State Visually-Evoked Potential Stimuli in Virtual Reality
J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, T.Kosch, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM In-Cooperation AHs '22, Munich, Germany
In Virtual Reality (VR), Steady-State-Visual Evoked Potentials (SSVEPs) can be used to interact with the virtual environment using brain signals. However, the design of SSVEP-eliciting stimuli often does not match the virtual environment, and thus, disrupts the virtual experience. In this paper, we investigate stimulus designs with varying suitability to blend in virtual environments. Therefore, we created differently-shaped, virtual butterflies...

Understanding Shoulder Surfer Behavior Using Virtual Reality
Y.Abdrabou, R.Rivu, T.Ammar, J.Liebers, A.Saad, C.Liebers, U.Gruenefeld, P.Knierim, M.Khamis, V.Mäkelä, S.Schneegass, and F.AltPublished Poster at IEEE VR '22, Christchurch, New Zealand
We explore how attackers behave during shoulder surfing. Unfortunately, such behavior is challenging to study as it is often opportunistic and can occur wherever potential attackers can observe other people’s private screens. Therefore, we investigate shoulder surfing using virtual reality (VR)...
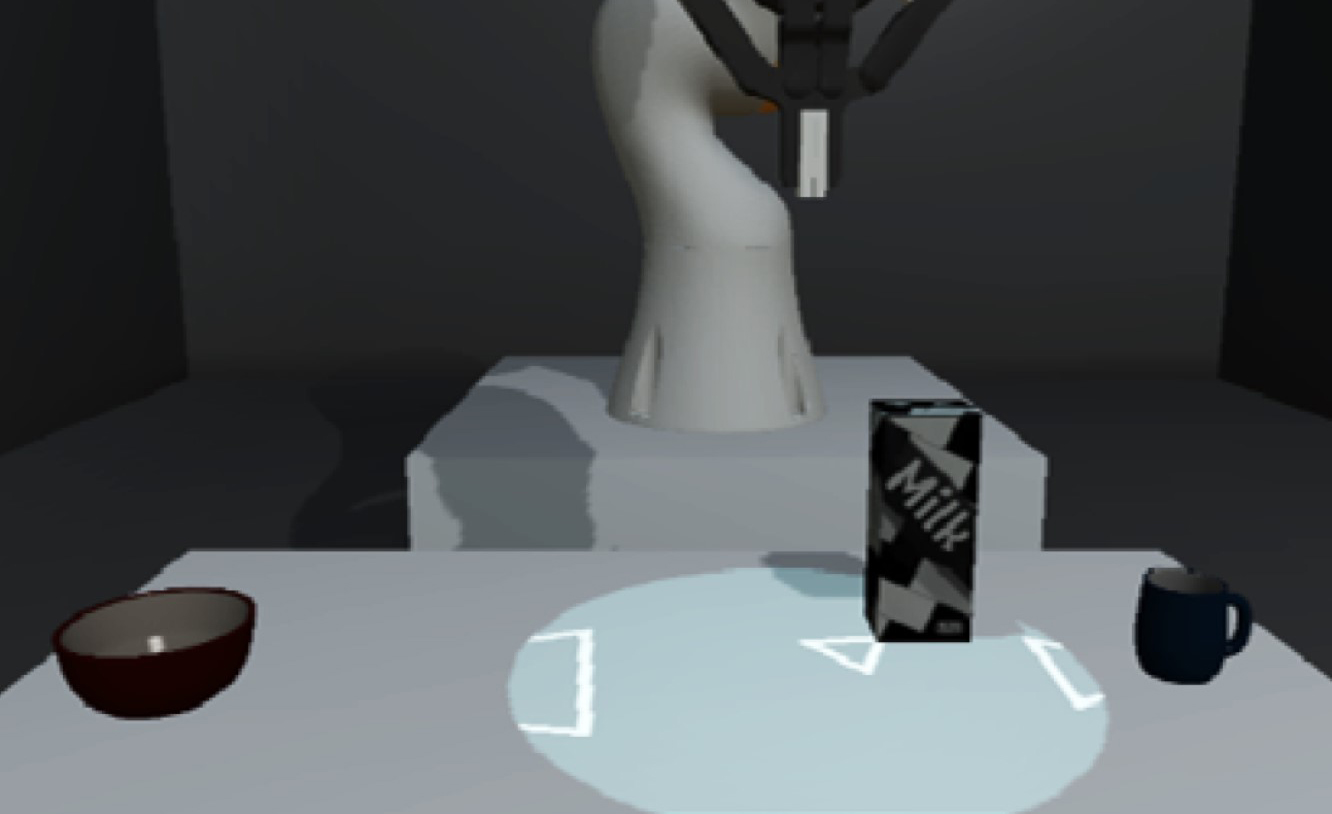

My Caregiver the Cobot: Comparing Visualization Techniques to Effectively Communicate Cobot Perception to People with Physical Impairments
M.Pascher, K.Kronhardt, T.Franzen, U.Gruenefeld, S.Schneegass, and J.GerkenPublished Journal Article at MDPI Sensors '22
Nowadays, robots are found in a growing number of areas where they collaborate closely with humans. Enabled by lightweight materials and safety sensors, these cobots are gaining increasing popularity in domestic care, where they support people with physical impairments in their everyday lives. However, when cobots perform actions autonomously, it remains challenging for human collaborators to understand and predict their behavior,...
2021
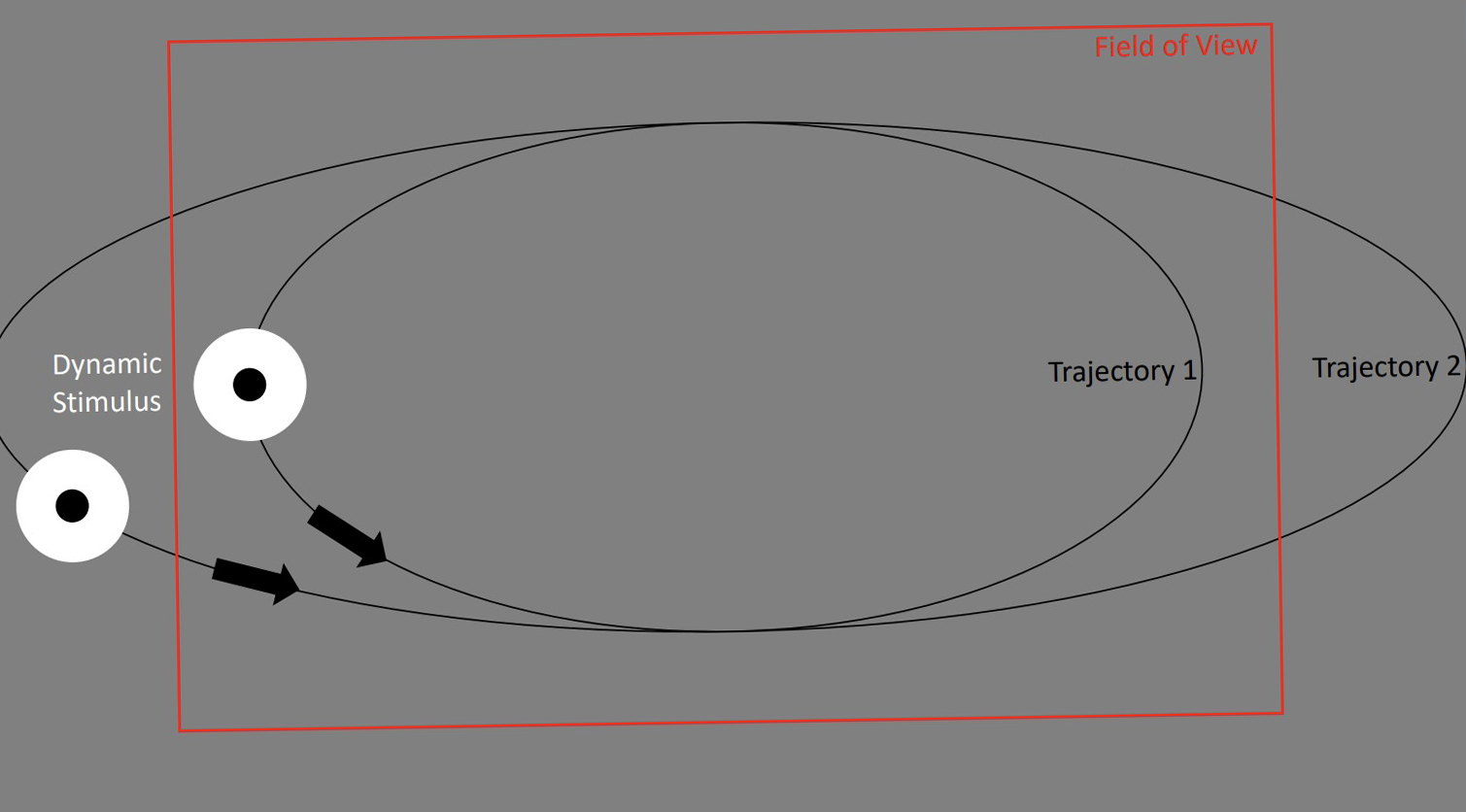
Using Gaze Behavior and Head Orientation for Implicit Identification in Virtual Reality
J.Liebers, P.Horn, C.Burschik, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM VRST '21, Osaka, Japan
Identifying users of a Virtual Reality (VR) headset provides designers of VR content with the opportunity to adapt the user interface, set user-specific preferences, or adjust the level of difficulty either for games or training applications. While most identification methods currently rely on explicit input, implicit user identification is less disruptive and does not impact the immersion of the users. In this work, we introduce a biometric identification system that employs the user’s gaze behavior as a unique, individual characteristic...
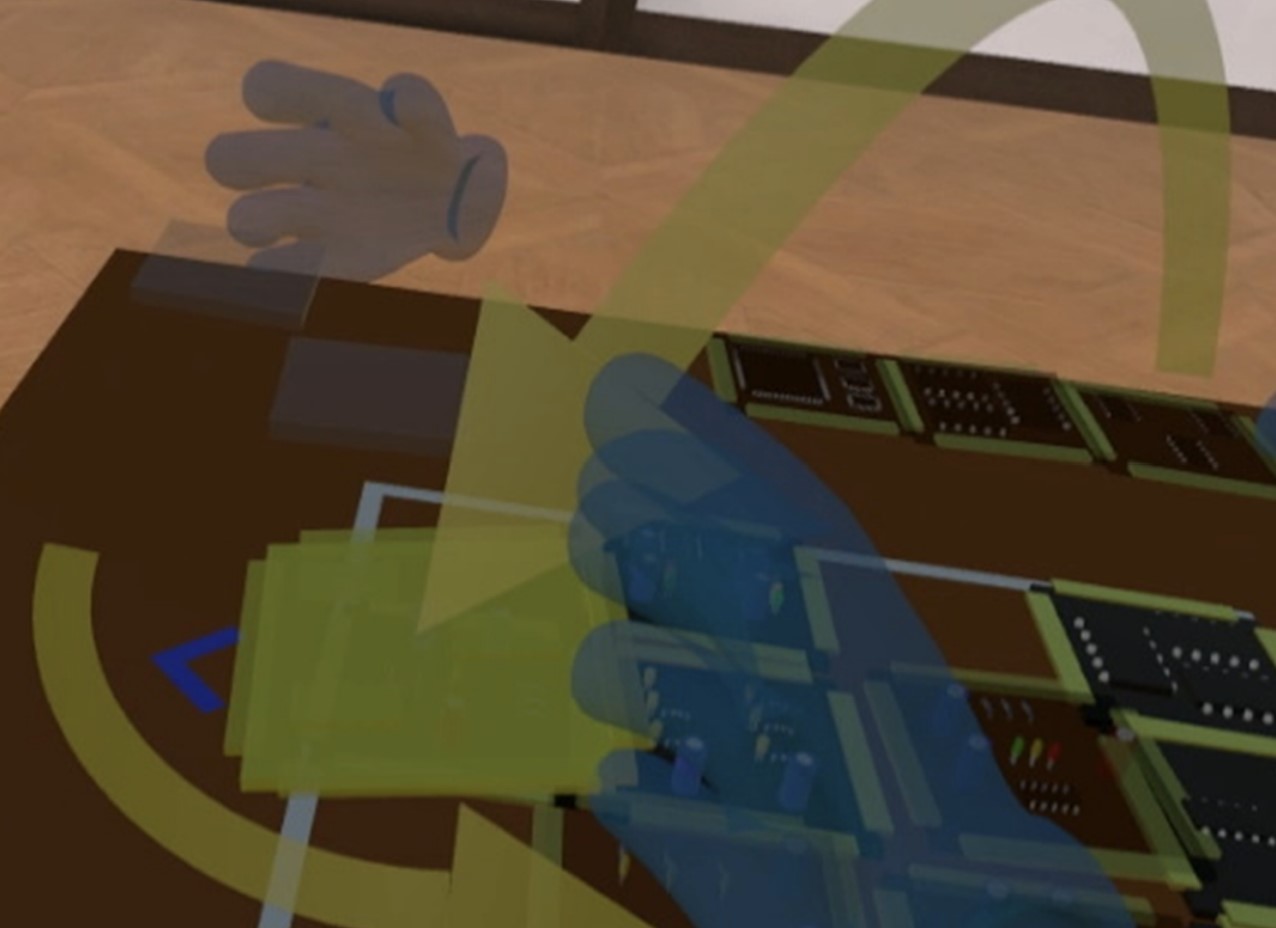

I’m in Control! Transferring Object Ownership Between Remote Users with Haptic Props in Virtual Reality
J.Auda, L.Busse, K.Pfeuffer, U.Gruenefeld, R.Rivu, F.Alt, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at SUI '21, Virtual Conference
Virtual Reality (VR) remote collaboration is becoming more and more relevant in a wide range of scenarios, such as remote assistance or group work. A way to enhance the user experience is using haptic props that make virtual objects graspable. But physical objects are only present in one location and cannot be manipulated directly by remote users. We explore different strategies to handle ownership of virtual objects enhanced by haptic props...
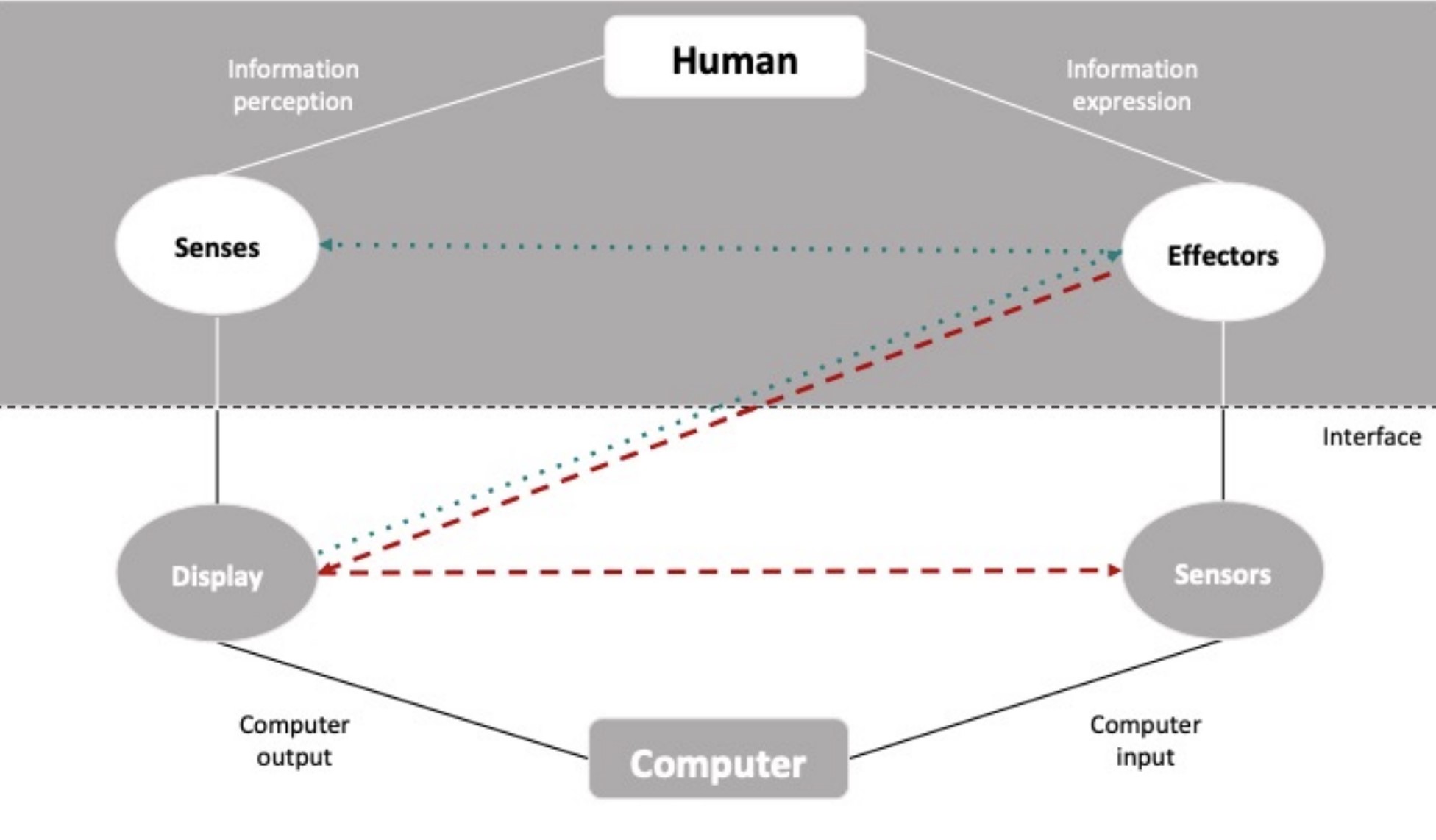
Towards a Universal Human-Computer Interaction Model for Multimodal Interactions
S.Faltaous, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at MuC '21, Ingolstadt, Germany
Models in HCI describe and provide insights into how humans use interactive technology. They are used by engineers, designers, and developers to understand and formalize the interaction process. At the same time, novel interaction paradigms arise constantly introducing new ways of how interactive technology can support humans. In this work, we look into how these paradigms can be described using the classical HCI model...
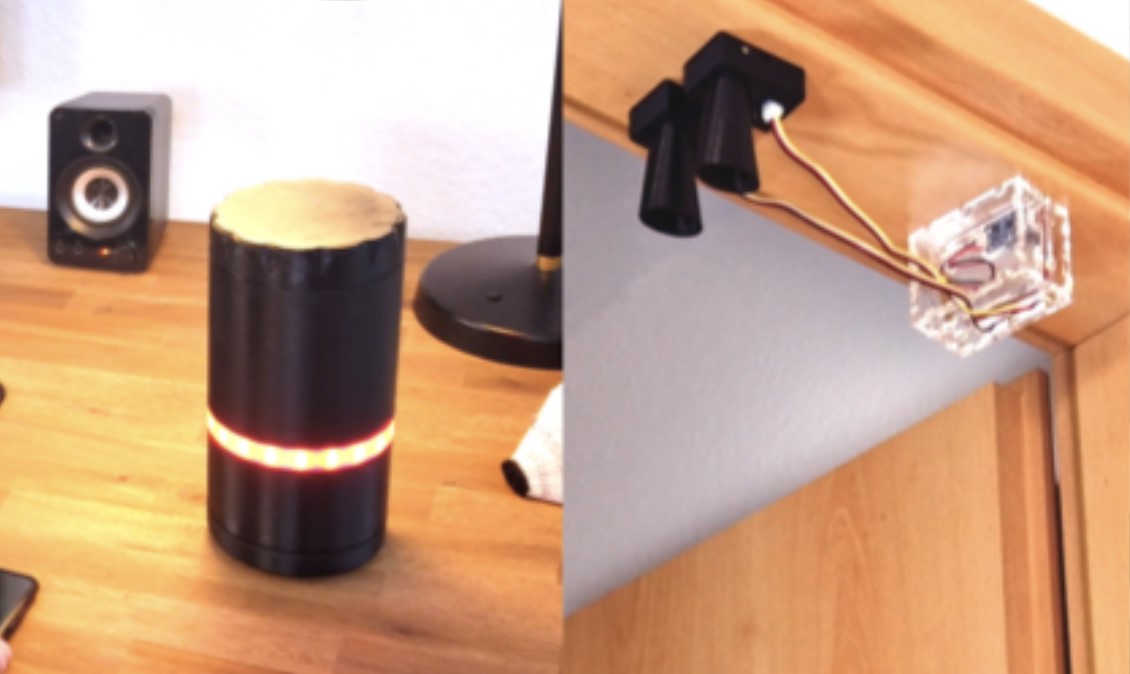

Wisdom of the IoT Crowd: Envisioning a Smart Home-based Nutritional Intake Monitoring System
S.Faltaous, S.Janzon, R.Heger, M.Strauss, P.Golkar, M.Viefhaus, M.Prochazka, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at MuC '21, Ingolstadt, Germany
Obesity and overweight are two factors linked to various health problems that lead to death in the long run. Technological advancements have granted the chance to create smart interventions. These interventions could be operated by the Internet of Things (IoT) that connects different smart home and wearable devices, providing a large pool of data. In this work, we use IoT with different technologies to present an exemplary nutrition monitoring intake system...
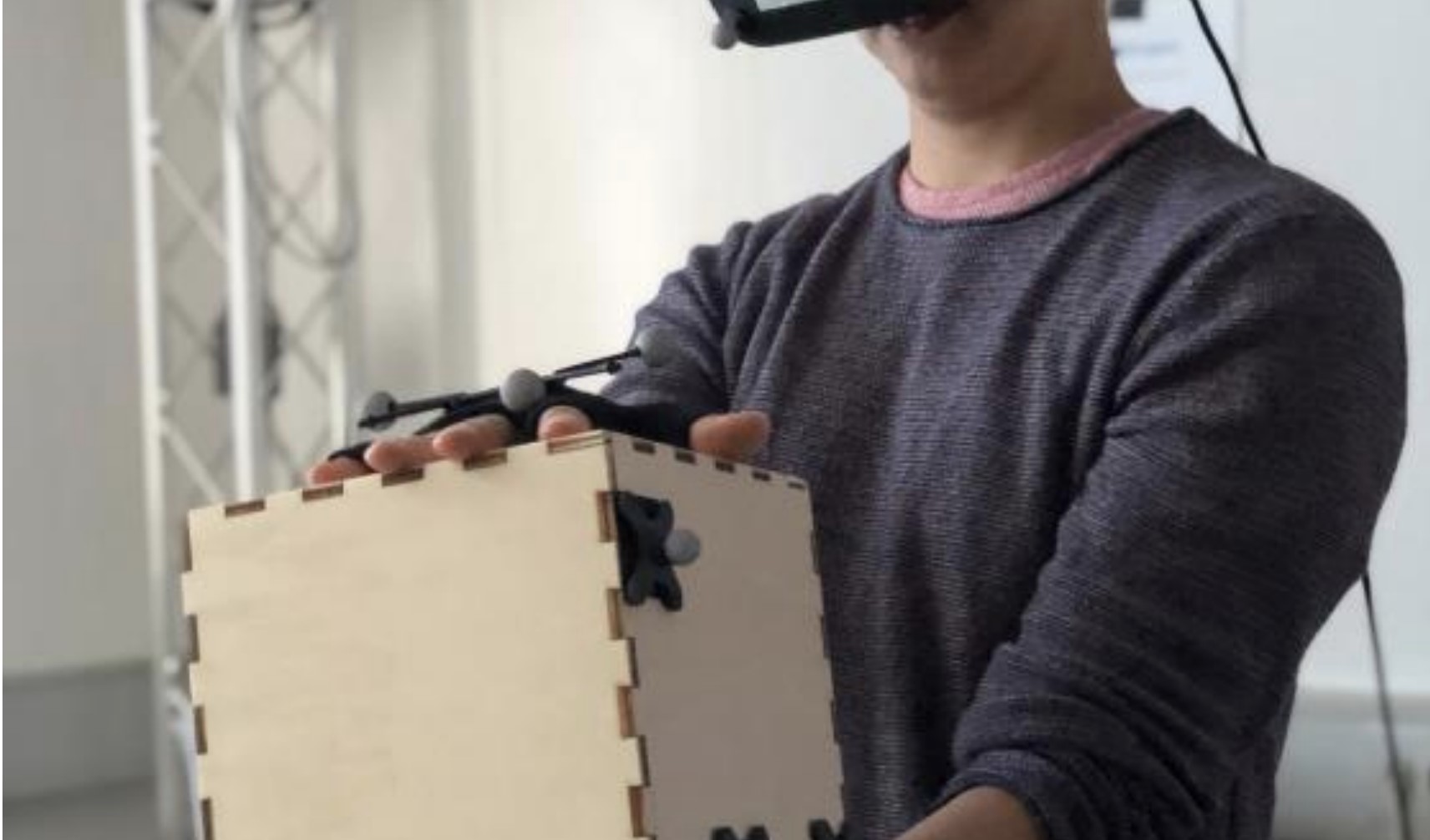

Enabling Reusable Haptic Props for Virtual Reality by Hand Displacement
J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at MuC '21, Ingolstadt, Germany
Virtual Reality (VR) enables compelling visual experiences. However, providing haptic feedback is still challenging. Previous work suggests utilizing haptic props to overcome such limitations and presents evidence that props could function as a single haptic proxy for several virtual objects. In this work, we displace users’ hands to account for virtual objects that are smaller or larger...
VRSketch: Investigating 2D Sketching in Virtual Reality with Different Levels of Hand and Pen Transparency
J.Auda, R.Heger, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at INTERACT '21, Bari, Italy
Sketching is a vital step in design processes. While analog sketching on pen and paper is the defacto standard, Virtual Reality (VR) seems promising for improving the sketching experience. It provides myriads of new opportunities to express creative ideas. In contrast to reality, possible drawbacks of pen and paper drawing can be tackled by altering the virtual environment. In this work, we investigate how hand and pen transparency...

VR4Sec: 1st International Workshop on Security for XR and XR for Security
S.Schneegass, M.Khamis, F.Alt, U.Gruenefeld, K.Marky, A.Saad, J.Liebers, J.Auda, F.Mathis, and L.MeckePublished Workshop at SOUPS '21, Virtual Event
Augmented and Virtual Reality (XR) technologies are finding their way into users’ everyday life. Contexts of use are home entertainment or professional collaboration, among others. The increasing interest in XR technology raises a need for the community to focus more strongly on XR aspects related to usable security and privacy. Additionally, XR technologies provide promising opportunities to study usable security and privacy topics...
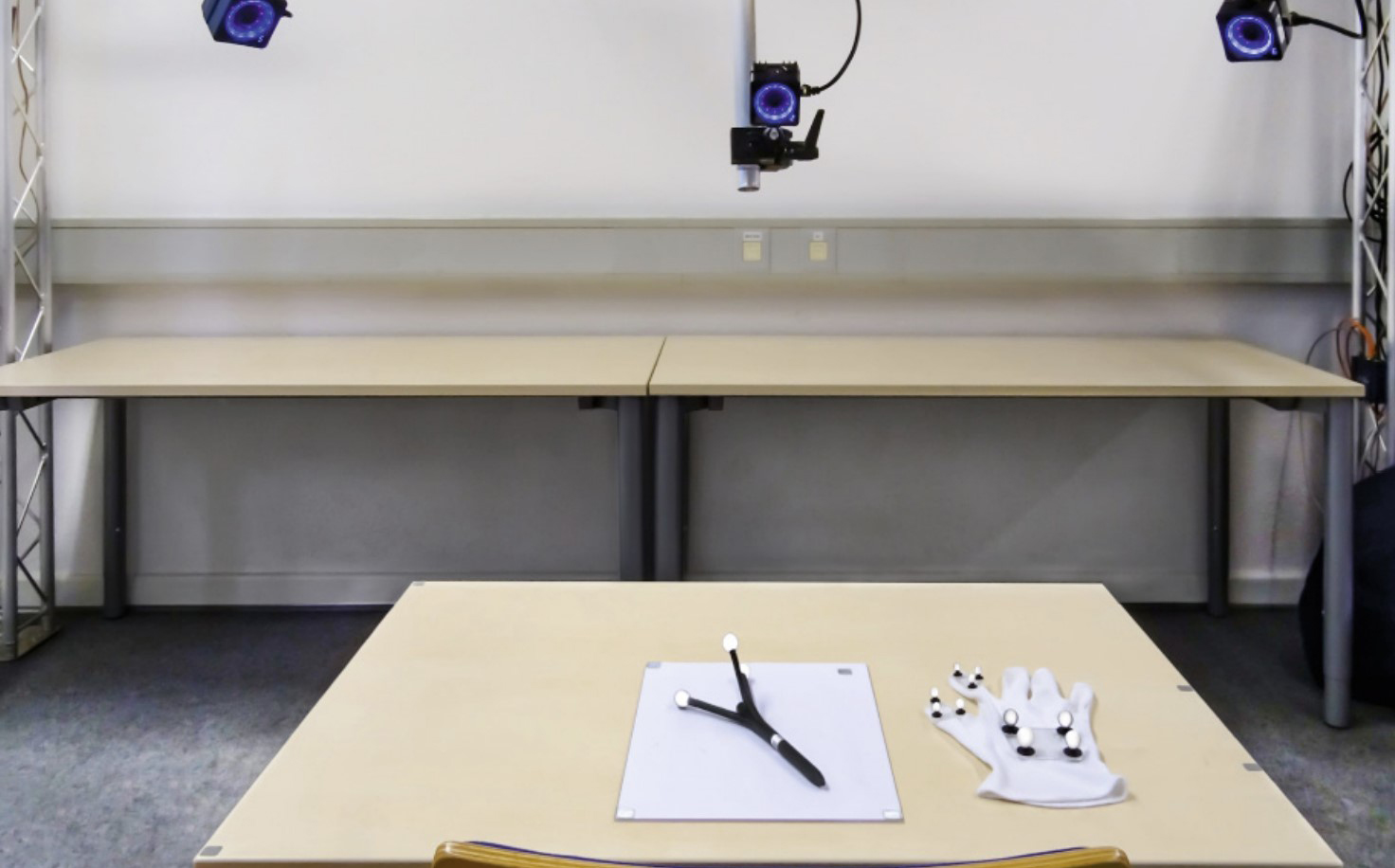
Understanding User Identification in Virtual Reality Through Behavioral Biometrics and the Effect of Body Normalization
J.Liebers, M.Abdelaziz, L.Mecke, A.Saad, J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, F.Alt, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM CHI '21, Yokohama, Japan
Virtual Reality (VR) is becoming increasingly popular both in the entertainment and professional domains.
Behavioral biometrics have recently been investigated as a means to continuously and implicitly identify users in VR.
Applications in VR can specifically benefit from this, for example, to adapt virtual environments and
user interfaces...

Understanding Bystanders’ Tendency to Shoulder Surf Smartphones Using 360-degree Videos in Virtual Reality
A.Saad, J.Liebers, U.Gruenefeld, F. Alt, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at MobileHCI '21, Toulouse, France
Shoulder surfing is an omnipresent risk for smartphone users. However, investigating these attacks in the wild is difficult because of either privacy concerns, lack of consent, or the fact that asking for consent would influence people’s behavior (e.g., they could try to avoid looking at smartphones). Thus, we propose utilizing 360-degree videos in Virtual Reality (VR), recorded in staged real-life situations on public transport...
2020
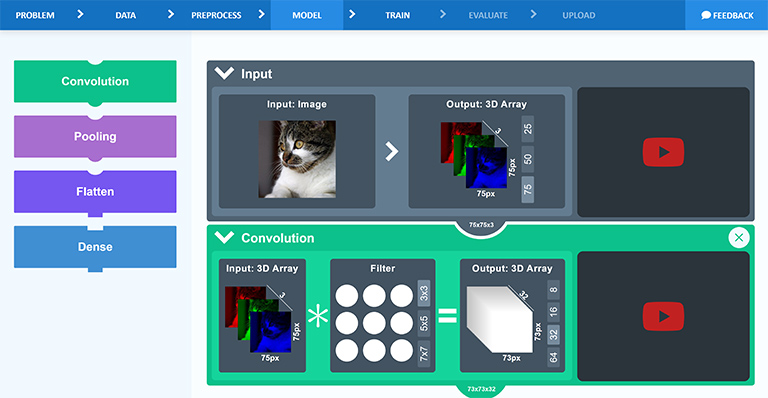
Demystifying Deep Learning: Developing and Evaluating a User-Centered Learning App for Beginners to Gain Practical Experience
S.Schultze, U.Gruenefeld, and S.BollPublished Journal Article at i-com '21
Deep Learning has revolutionized Machine Learning, enhancing our ability to solve complex computational problems.
From image classification to speech recognition, the technology can be beneficial in a broad range of scenarios.
However, the barrier to entry is quite high, especially when programming skills are missing...
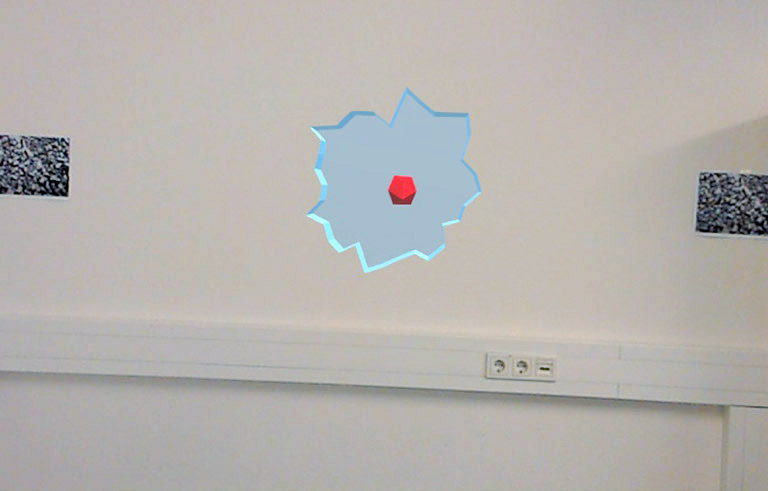

Behind the Scenes: Comparing X-Ray Visualization Techniques in Head-mounted Optical See-through Augmented Reality
U.Gruenefeld, Y.Brück, and S.BollPublished Paper at ACM MUM '20, Essen, Germany
Locating objects in the environment can be a difficult task, especially when the objects are occluded.
With Augmented Reality, we can alternate our perceived reality by augmenting it with visual cues or
removing visual elements of reality, helping users to locate occluded objects. However, to our knowledge,
it has not yet been evaluated which visualization technique works best for estimating the distance and size
of occluded objects...
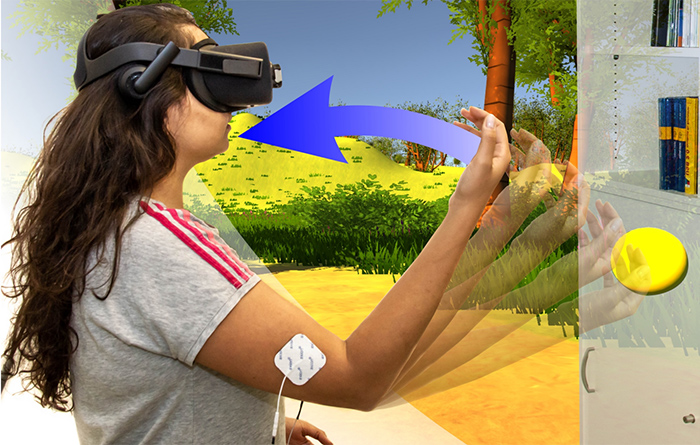

SaVR: Increasing Safety in Virtual Reality Environments via Electrical Muscle Stimulation
S.Faltaous, J.Neuwirth, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Paper at ACM MUM '20, Essen, Germany
One of the main benefits of interactive Virtual Reality (VR) applications is that they provide a high sense of immersion.
As a result, users lose their sense of real-world space which makes them vulnerable to collisions with real-world objects.
In this work, we propose a novel approach to prevent such collisions using Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)...

Time is money! Evaluating Augmented Reality Instructions for Time-Critical Assembly Tasks
J.Illing, P.Klinke, U.Gruenefeld, M.Pfingsthorn, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM MUM '20, Essen, Germany
Manual assembly tasks require workers to precisely assemble parts in 3D space. Often additional time pressure increases the
complexity of these tasks even further (e.g., adhesive bonding processes). Therefore, we investigate how Augmented Reality (AR)
can improve workers' performance in time and spatial dependent process steps. In a user study, we compare three conditions:
instructions presented on (a) paper, (b) a camera-based see-through tablet, and (c) a head-mounted AR device...
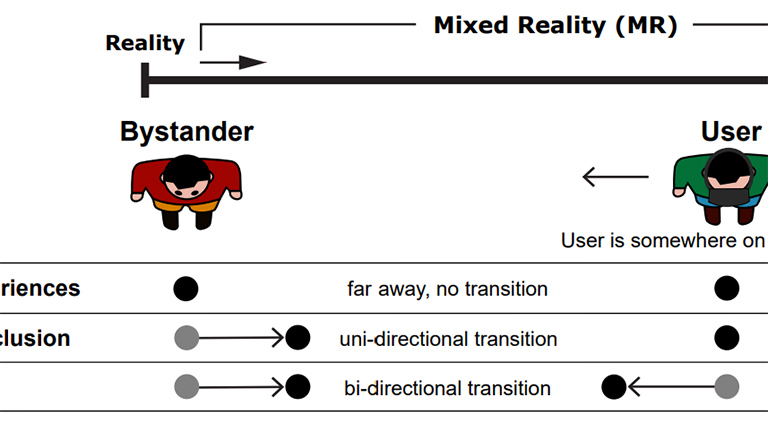
It Takes Two To Tango: Conflicts Between Users on the Reality-Virtuality Continuum and Their Bystanders
J.Auda, U.Gruenefeld, and S.MayerPublished Workshop Paper at ACM ISS '20, Lisbon, Portugal
Over the last years, Augmented and Virtual Reality technology became more immersive. However, when users immerse themselves
in these digital realities, they detach from their real-world environments. This detachment creates conflicts that are problematic
in public spaces such as planes but also private settings. Consequently, on the one hand, the detaching from the world creates an
immerse experience for the user, and on the other hand, this creates a social conflict with bystanders...
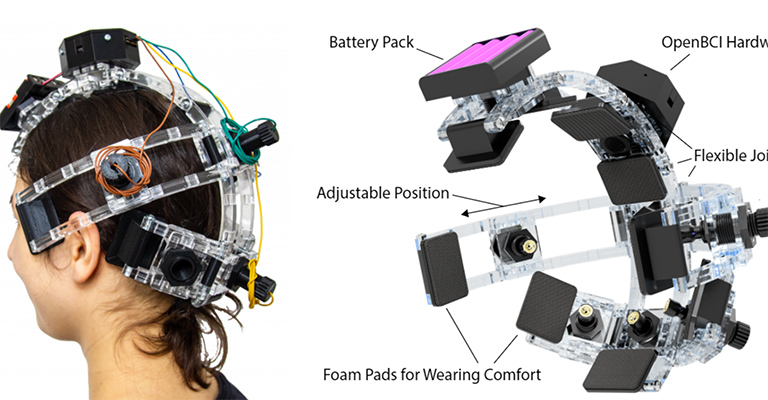
EasyEG: A 3D-printable Brain-Computer Interface
J.Auda, R.Heger, T.Kosch, U.Gruenefeld, and S.SchneegassPublished Poster at ACM UIST '20, Minnesota, USA
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) are progressively adopted by the consumer market, making them available for a variety of use-cases.
However, off-the-shelf BCIs are limited in their adjustments towards individual head shapes, evaluation of scalp-electrode contact,
and extension through additional sensors. This work presents EasyEG, a BCI headset that is adaptable to individual head shapes and
offers adjustable electrode-scalp contact to improve measuring quality...

Demystifying Deep Learning: Developing a Learning App for Beginners to Gain Practical Experience
S.Schultze, U.Gruenefeld, and S.BollPublished Workshop Paper at MuC '20, Magdeburg, Germany
Deep learning has revolutionized machine learning, enhancing our ability to solve complex computational problems.
From image classification to speech recognition, the technology can be beneficial in a broad range of scenarios.
However, the barrier to entry is quite high, especially when programming skills are missing. In this paper,
we present the development of a learning application for beginners...
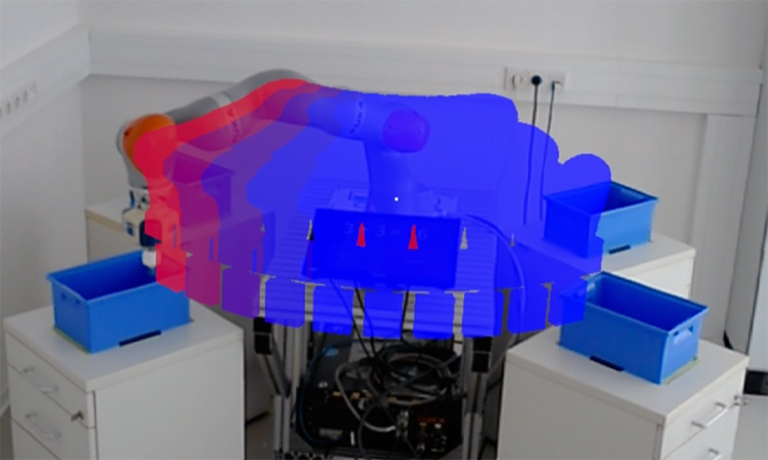
Mind the ARm: Realtime Visualization of Robot Motion Intent in Head-mounted Augmented Reality
U.Gruenefeld, L.Prädel, J.Illing, T.C.Stratmann, S.Drolshagen, and M.PfingsthornPublished Paper at MuC '20, Magdeburg, Germany
Established safety sensor technology shuts down industrial robots when a collision is detected, causing preventable
loss of productivity. To minimize downtime, we implemented three Augmented Reality (AR) visualizations (Path, Preview, and Volume)
which allow users to understand robot motion intent and give way to the robot. We compare the different visualizations
in a user study in which a small cognitive task is performed...

HiveFive: Immersion Preserving Attention Guidance
in Virtual Reality
D.Lange, T.C.Stratmann, U.Gruenefeld, and S.BollPublished Paper at ACM CHI '20, Honolulu, Hawaii
Recent advances in Virtual Reality (VR) technology, such as larger fields of view,
have made VR increasingly immersive. However, a larger field of view often results
in a user focusing on certain directions and missing relevant content presented
elsewhere on the screen. With HiveFive, we propose a technique that uses swarm motion
to guide user attention...
2019
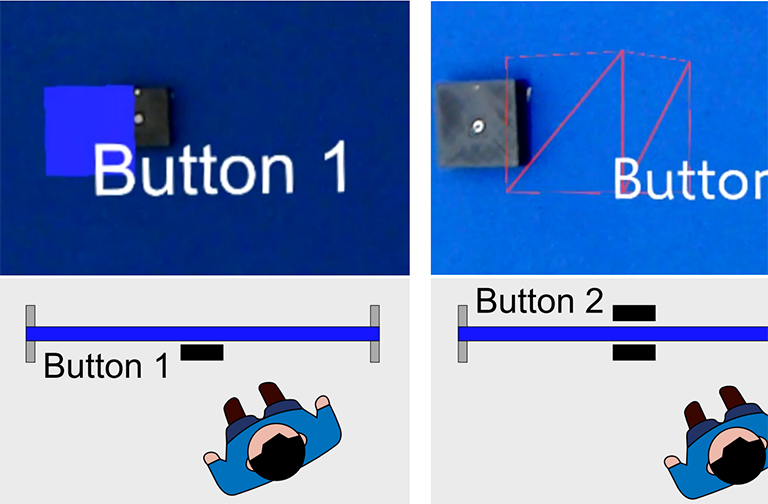
Locating Nearby Physical Objects in Augmented Reality
U.Gruenefeld, L.Prädel, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM MUM '19, Pisa, Italy
Locating objects in physical environments can be an exhausting and
frustrating task, particularly when these objects are out of the user's view
or occluded by other objects. With recent advances in Augmented Reality (AR),
these environments can be augmented to visualize objects for which the user
searches. However, it is currently unclear which visualization strategy can best
support users in locating these objects.

VRoad: Gesture-based Interaction Between Pedestrians and Automated Vehicles in Virtual Reality
U.Gruenefeld, S.Weiß, A.Löcken, I.Virgilio, A.Kun, and S.BollPublished Poster at AutoUI '19, Utrecht, Netherlands
As a third party to both automated and non-automated vehicles, pedestrians are among the most vulnerable
participants in traffic. Currently, there is no way for them to communicate their intentions to an automated vehicle (AV).
In this work, we explore the interactions between pedestrians and AVs at unmarked crossings.
We propose...
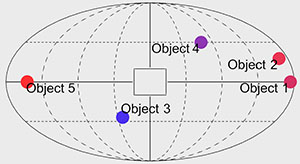
Improving Search Time Performance for Locating
Out-of-View Objects in Augmented Reality
U.Gruenefeld, L.Prädel, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at MuC '19, Hamburg, Germany
🏆 Honorable Mention Award
Locating virtual objects (e.g., holograms) in head-mounted Augmented Reality (AR)
can be an exhausting and frustrating task. This is mostly due to the limited
field of view of current AR devices, which amplify the problem of objects
receding from view. In previous work, EyeSee360...

ChalkboARd: Exploring Augmented Reality for Public Displays
U.Gruenefeld, T.Wolff, N.Diekmann, M.Koelle, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM PerDis '19, Palermo, Italy
Augmented Reality (AR) devices and applications are gaining in popularity,
and - with recent trends such as Pokemon Go - are venturing into public spaces
where they become more and more pervasive. In consequence, public AR
displays might soon be part of our cityscapes and may impact on our
everyday view of the world. In this work, we present ChalkboARd, a
prototype of an AR-enabled public display...

Comparing Techniques for Visualizing Moving Out-of-View Objects in Head-mounted Virtual Reality
U.Gruenefeld, I.Koethe, D.Lange, S.Weiß, and W.HeutenPublished short paper at IEEE VR '19, Osaka, Japan
Current head-mounted displays (HMDs) have a limited field-of-view (FOV).
A limited FOV further decreases the already restricted human visual range and amplifies
the problem of objects receding from view (e.g., opponents in computer games).
However, there is no previous work that investigates how to best perceive moving out-of-view
objects...
2018

Mobile Bridge - A Portable Design Simulator for
Ship Bridge Interfaces
T.C.Stratmann, U.Gruenefeld, J.Stratmann, S.Schweigert, A.Hahn, and S.BollPublished Journal Article at TransNav '19
Developing new software components for ship bridges is challenging.
Mostly due to high costs of testing these components in realistic environments.
To reduce these costs the development process is divided into different stages.
Whereas, the final test on a real ship bridge is the last step in this process.
However, by dividing the development process...
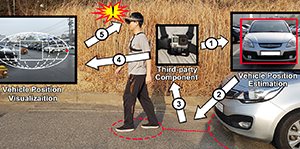
Ensuring Safety in Augmented Reality from Trade-off Between Immersion and Situation Awareness
J.Jung, H.Lee, J.Choi, A.Nanda, U. Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, and W. HeutenPublished Paper at IEEE ISMAR '18, Munich, Germany
Although the mobility and emerging technology of augmented reality (AR) have brought significant entertainment and convenience in everyday life, the use of AR is becoming a social problem as the accidents caused by a shortage of situation awareness due to an immersion of AR are increasing. In this paper, we address the trade-off between immersion and situation awareness as the fundamental factor of the AR-related accidents.

Guiding Smombies: Augmenting Peripheral Vision with Low-Cost Glasses to Shift the Attention of Smartphone Users
U.Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, J.Jung, H.Lee, J.Choi, A.Nanda, and W.HeutenPublished Poster at IEEE ISMAR '18, Munich, Germany
Over the past few years, playing Augmented Reality (AR) games on smartphones has steadily been gaining
in popularity (e.g., Pokémon Go). However, playing these games while navigating traffic is highly dangerous
and has led to many accidents in the past. In our work, we aim to augment peripheral vision of pedestrians
with low-cost glasses to support them in critical traffic encounters. Therefore, we developed a lo-fi prototype
with peripheral displays. We technically improved...

Juggling 4.0: Learning Complex Motor Skills with Augmented Reality Through the Example of Juggling
B.Meyer, P.Gruppe, B.Cornelsen, T.C.Stratmann, U.Gruenefeld, and S.BollPublished Poster at ACM UIST '18, Berlin, Germany
Learning new motor skills is a problem that people are constantly confronted with (eg to learn a new kind of sport).
In our work, we investigate to which extent the learning process of a motor sequence can be optimized with the help
of Augmented Reality as a technical assistant. Therefore, we propose an approach that divides the problem...
Identification of Out-of-View Objects in Virtual Reality
U.Gruenefeld, R.von Bargen, and W.HeutenPublished Poster at ACM SUI '18, Berlin, Germany
Current Virtual Reality (VR) devices have limited fields-of-view (FOV). A limited FOV amplifies
the problem of objects receding from view. In previous work, different techniques have been
proposed to visualize the position of objects out of view. However, these techniques do not allow
to identify these objects. In this work, we compare three different ways...
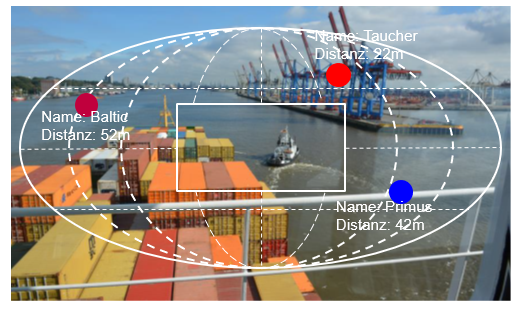
Investigations on Container Ship Berthing from the Pilot’s Perspective: Accident Analysis, Ethnographic Study, and ...
U. Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, Y.Brueck, A.Hahn, S.Boll, and W.HeutenPublished Journal Article at TransNav '19
In recent years, container ships have had to transport more and more goods due to constantly growing demand.
Therefore, the container ships for carrying these goods are growing in size, while the harbors fall short
in adapting to these changes. As a result, the berthing of these container ships in harbors has become more challenging
for harbor pilots.
Where to Look: Exploring Peripheral Cues for Shifting Attention to Spatially Distributed Out-of-View Objects
U. Gruenefeld, A.Löcken, Y.Brueck, S.Boll, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM AutoUI '18, Toronto, Canada
Knowing the locations of spatially distributed objects is important in many different scenarios
(e.g., driving a car and being aware of other road users). In particular, it is critical for
preventing accidents with objects that come too close (e.g., cyclists or pedestrians). In this paper,
we explore how peripheral cues can shift a user's attention towards spatially distributed out-of-view objects.
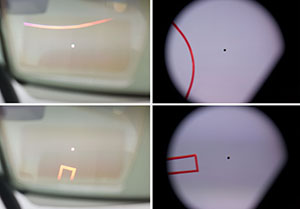
Beyond Halo and Wedge: Visualizing Out-of-View Objects on Head-mounted Virtual and Augmented Reality Devices
U.Gruenefeld, A.El Ali, S.Boll, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM MobileHCI '18, Barcelona, Spain
Head-mounted devices (HMDs) for Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) enable us to alter
our visual perception of the world. However, current devices suffer from a limited field of view (FOV),
which becomes problematic when users need to locate out of view objects (e.g., locating points-of-interest
during sightseeing). To address this, ...

RadialLight: Exploring Radial Peripheral LEDs for Directional Cues in Head-Mounted Displays
U.Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, A.El Ali, S.Boll, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM MobileHCI '18, Barcelona, Spain
Current head-mounted displays (HMDs) for Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have a
limited field-of-view (FOV). This limited FOV further decreases the already restricted human visual range
and amplifies the problem of objects going out of view. Therefore, we explore the utility of augmenting HMDs
with RadialLight, ...

MonoculAR: A Radial Light Display to Point Towards Out-of-View Objects on Augmented Reality Devices
U.Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, L.Prädel, and W.HeutenPublished Poster at ACM MobileHCI '18, Barcelona, Spain
Present head-mounted displays (HMDs) for Augmented Reality (AR) devices have narrow fields-of-view (FOV).
The narrow FOV further decreases the already limited human visual range and worsens the problem of objects
going out of view. Therefore, we explore the utility of augmenting head-mounted AR devices with MonoculAR, ...

BuildingBlocks: Head-mounted Virtual Reality for Robot Interaction in Large Non-Expert Audiences
U. Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, L.Prädel, M.Pfingsthorn, and W.HeutenPublished Workshop Paper at ACM MobileHCI '18', Barcelona, Spain
Virtual Reality (VR) technology empowers users to experience and manipulate virtual environments in a novel way.
Further, by using digital twins of real world objects it is also possible to extend the reach of interaction to reality.
In this work, we explore how users interact with a robot arm and its programming by using a digital representation in VR.
In particular, we were interested...
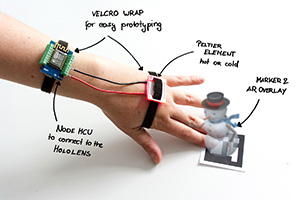
Augmenting Augmented Reality
U.Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, J.Auda, M.Koelle, S.Schneegass, and W.HeutenPublished Tutorial at ACM MobileHCI '18, Barcelona, Spain
Today’s Augmented Reality (AR) devices enable users to interact almost naturally with their surroundings,
e.g., by pinning digital content onto real-world objects. However, current AR display are mostly limited
to optical and video see-through technologies. Nevertheless, extending Augmented Reality (AR) beyond screens
by accommodating additional modalities (e.g., smell or haptics)...
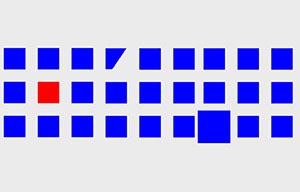
Effective Visualization of Time-Critical Notifications
in Virtual Reality
U.Gruenefeld, M.Harre, T.C.Stratmann, A.Lüdtke, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at MuC '18, Dresden, Germany
Virtual Reality (VR) devices empower users to be fully immersed into a virtual environment.
However, time-critical notifications must be perceived as quickly and correctly as possible.
Especially, if they indicate risk of injury (e.g., bumping into walls). Compared to displays
used in previous work to investigate fast response times, immersion...

EyeMR - Low-cost Eye-Tracking for Rapid-prototyping in Head-mounted Mixed Reality
T.C.Stratmann, U.Gruenefeld, and S.BollPublished Poster at ACM ETRA '18, Warsaw, Poland
Mixed Reality devices can either augment reality (AR) or create completely virtual realities (VR).
Combined with head-mounted devices and eye-tracking, they enable users to interact with these systems
in novel ways. However, current eye-tracking systems are expensive and limited in the interaction
with virtual content. In this paper, we present EyeMR, ...
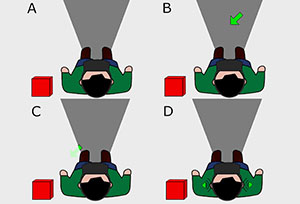
FlyingARrow: Pointing Towards Out-of-View Objects on Augmented Reality Devices
U.Gruenefeld, D.Lange, L.Hammer, S.Boll, and W.HeutenPublished Paper at ACM PerDis '18, Munich, Germany
Augmented Reality (AR) devices empower users to enrich their surroundings by pinning digital content
onto real world objects. However, current AR devices suffer from having small fields of view,
making the process of locating spatially distributed digital content similar to looking through a keyhole.
Previous solutions are not suitable...

Exploring Vibrotactile and Peripheral Cues for
Spatial Attention Guidance
T.C.Stratmann, A.Löcken, U.Gruenefeld, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Paper at ACM PerDis '18, Munich, Germany
For decision making in monitoring and control rooms situation awareness is key. Given the often spacious and complex environments,
simple alarms are not sufficient for attention guidance (e.g., on ship bridges). In our work, we explore shifting attention
towards the location of relevant entities in large cyber-physical systems. Therefore, we used...
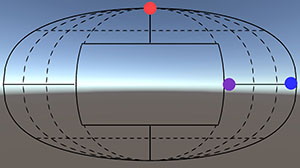
EyeSeeX: Visualization of Out-of-View Objects on Small Field-of-View Augmented and Virtual Reality Devices
U.Gruenefeld, D.Hsiao, and W.HeutenPublished Demo at ACM PerDis '18, Munich, Germany
Recent advances in Virtual and Augmented Reality technology enable a variety of new applications
(e.g., multi-player games in real environments). However, current devices suffer from having small fields of view,
making the process of locating spatially distributed digital content similar to looking through a keyhole.
In this work, we present EyeSeeX...
2017
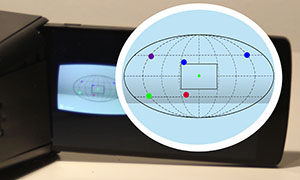
EyeSee360: Designing a Visualization Technique for Out-of-View Objects in Head-mounted Augmented Reality
U. Gruenefeld, D.Ennenga, A.El Ali, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Paper at ACM SUI '17, Brighton, United Kingdom
🏆 Honorable Mention Award
Head-mounted displays allow user to augment reality or dive into a virtual one.
However, these 3D spaces often come with problems due to objects that may be out of view.
Visualizing these out-of-view objects is useful under certain scenarios, such as situation
monitoring during ship docking. To address this, we designed a lo-fi prototype of our EyeSee360 system,
and based on user feedback, subsequently...
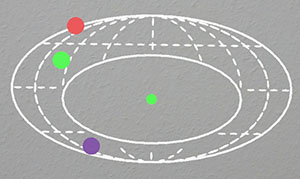
EyeSee: Beyond Reality with Microsoft Hololens
U.Gruenefeld, D.Hsiao, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Demo at ACM SUI '17, Brighton, United Kingdom
Head-mounted Augmented Reality (AR) devices allow overlaying digital information on the real world,
where objects may be out of view. Visualizing these out-of-view objects is useful under certain scenarios.
To address this, we developed EyeSee360 in our previous work. However, our implementation of EyeSee360
was limited to video-see-through devices.
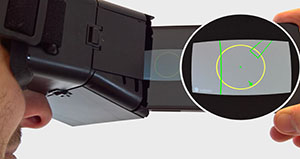
Visualizing Out-of-View Objects in Head-mounted
Augmented Reality
U. Gruenefeld, A.El Ali, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Late-Breaking Work at ACM MobileHCI '17, Vienna, Spain
Various off-screen visualization techniques that point to off-screen objects have been
developed for small screen devices. A similar problem arises with head-mounted Augmented Reality (AR)
with respect to the human field-of-view, where objects may be out of view. Being able to detect
so-called out-of-view objects is useful for certain scenarios...

PeriMR: A Prototyping Tool for Head-mounted Peripheral Light Displays in Mixed Reality
U.Gruenefeld, T.C.Stratmann, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Demo at ACM MobileHCI '17, Vienna, Spain
Nowadays, Mixed and Virtual Reality devices suffer from a field of view that is too small
compared to human visual perception. Although a larger field of view is useful
(e.g., conveying peripheral information or improving situation awareness), technical limitations
prevent the extension of the field-of-view. A way to overcome these limitations...

Effects of Location and Fade-in Time of (Audio-)Visual Cues on Response Times and Success-rates in a Dual-task Experiment
A.Löcken, S.Blum, T.C.Stratmann, U.Gruenefeld, W.Heuten, S.Boll, and S.van de ParPublished Paper at ACM SAP '17, Cottbus, Germany
While performing multiple competing tasks at the same time, e.g., when driving,
assistant systems can be used to create cues to direct attention towards required information.
However, poorly designed cues will interrupt or annoy users and affect their performance.
Therefore, we aim to identify cues that are not missed and trigger...
2014
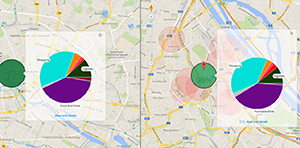
Swarming in the Urban Web Space to Discover the
Optimal Region
C.Kumar, U.Gruenefeld, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Paper at IEEE/WIC/ACM WI '14, Warsaw, Poland
People moving to a new place usually look for a suitable region with respect to their
multiple criteria of interests. In this work we map this problem to the migration behavior of other species
such as swarming, which is a collective behavior exhibited by animals of similar size which aggregate together,
milling about the same region. Taking the swarm intelligence perspective, we present a novel method...
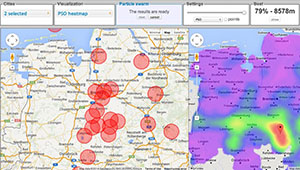
Characterizing the Swarm Movement on Map for
Spatial Visualization
C.Kumar, U.Gruenefeld, W.Heuten, and S.BollPublished Poster at IEEE TVCG '14, Paris, France
Visualization of maps to explore relevant geographic areas is one of the common practices in spatial decision scenarios.
However visualizing geographic distribution with multidimensional criteria becomes a nontrivial setup in the conventional point based mapspace.
In this work, we present a novel method to generalize frompoint data to spatial distributions, captivating on the swarm intelligence.
